Project Requirements
-
Build a basic hybrid file system that realizes the extensibility of cloud storage, the small random access speed of SSDs, the low operational cost of local SSDs, and the freedom of not having to worry about device endurance or reliability, all at a minimal cost. The idea is to have a size-based placement to leverage the high number of IO operations per second (IOPS) provided by SSDs and on-disk attribute replication of large files to avoid performing small IOs on Cloud storage.
-
Implement deduplication. Deduplication is basically CloudFS trying to discover duplication among unrelated files and store duplicate content only once. There are many ways one can find duplicate content, but each comes with a tradeoff. The one used by CloudFS is called content-based deduplication with a “given” minimum, maximum and average segment size. A segment is a “portion” or “chunk”of a file which is found depending on its content and not its relative position within the file.
-
Support snapshot operations of CloudFS
-
Support write-back caching with contents that persist a cross mounts and with no in-memory component. The process of taking a snapshot involves capturing the state of the entire file system at a given point in time and copying said state to the cloud, which is assumed to be reliable. After the snapshot is taken, the file system is available again for normal use.
-
When a snapshot is restored, all changes since the snapshot was taken should be undone, returning the file system to that point in time. In addition to creating and restoring snapshots, CloudFS supports installing (and uninstalling) them. By installing a snapshot, the user is able to browse the content of an existing snapshot without restoring it or altering the state of the file system. It creates a read-only folder of that snapshot at CloudFS root directory.
Project Details
-
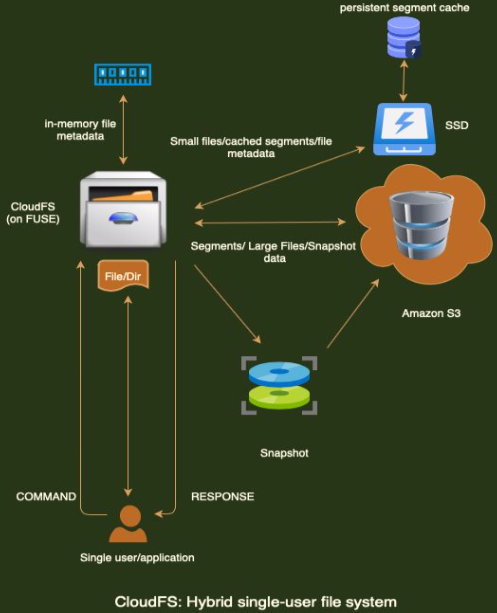
CloudFS is a single-user, single-threaded, local file system backed by a cloud service, and therefore a hybrid file system. It stores all file metadata and some file data (upto a given threshold file size) on a local drive, and the rest of the file data using a cloud object storage service, Amazon S3.
-
It is built using the FUSE (Filesystem in USErspace) software interface. It consists of four major components:
- A core file system leveraging the properties of local SSD and cloud storage for making data placement decisions, AKA threshold;
- A component that takes advantage of redundancy in data to reduce storage capacity, AKA deduplication;
- A component that adds the ability to create, delete, install, uninstall and restore file system snapshots while minimizing cloud storage costs;
- A component that uses local on-device caching to improve performance and reduce cloud operation costs.
-
CloudFS provides a mount-unmount consistency, but not crash consistency. The figure on the left pictorially summarizes the operations, design and capabilities of CloudFS.
-
The backend file system used by SSD is assumed to be ext4 FS. This project is divided into three major checkpoints, each implementing the four components of CloudFS stated above. The report is divided into three parts, one for each checkpoint.
-
My overall design goal was: “Keep it simple”.